
|
|||
|
| Home |
| About |
| Hobbies |
| Software |
| Hardware |
| ICT Hotlist |
| Purpose |

ICT-Hotlist Topic
Business Continuity Management: an introduction.

What is the purpose of Business Continuity Management?
The goal of a Business Continuity Manager is, within the limits and conditions formulated by company management, to take care that the normal activities of the company, organization or institution can (re-)start, within a stipulated time frame, when a calamity or disaster occurs. Governments pay special attention to information/data and ICT systems that receive, save, edit, view and send data as these are the most important resources for the contemporary business operations.
Business Continuity Management: some calamities we all can recognize.
Consequences of a calamity
The abruptness and the often large impact on the normal functioning of an organization can result in, among other things, the following:- Chaos and uncertainty
- Demotivated employees
- Services or products cannot be supplied (on time)
- Financial auditing is no longer possible
- Fraud
- Damage to Image/brand/reputation
- Information is no longer at hand
- Vital information is lost
- Injured or died (key) employees
What to do?
Awareness that a fire, power failure or other disaster not only affects your neighbour is the first step. Start with the questions "what am I going to do about it?" and "who is going to do it?". These articles may help getting you started:- Business Continuity Management: Escalation procedure (ICT).
- Business Continuity Management Example: selection process disaster / calamity preparation.
- Business Continuity Management Example: selection process failure preparation.
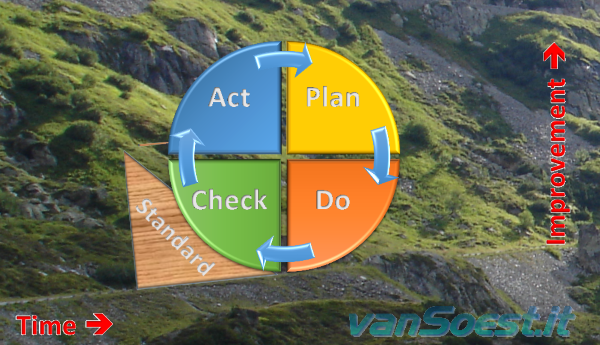
Deming Cycle of Continuous Improvement (Plan, Do, Check and Act) with consolidation.
Glossary
- Calamity:
- A calamity mostly arises from an incident of external origin that expands across multiple hardware systems, software
systems or even employees. These incidents include:
- Fire
- Economic boycotts
- Epidemics
- Hacking
- Floods
- Sabotage
- Software errors
- Storm damages
- Failing software updates
- Failure:
- Briefly formulated a failure is a confined problem that relates to one program or one hardware component. Solutions for failures are mostly found in redundancy and high availability systems ( HA )
You may vote your opinion about this article:





Scripts and programming examples disclaimer
Unless stated otherwise, the script sources and programming examples provided are copyrighted freeware. You may modify them, as long as a reference to the original code and hyperlink to the source page is included in the modified code and documentation. However, it is not allowed to publish (copies of) scripts and programming examples on your own site, blog, vlog, or distribute them on paper or any other medium, without prior written consent.Many of the techniques used in these scripts, including but not limited to modifying the registry or system files and settings, impose a risk of rendering the Operating System inoperable and loss of data. Make sure you have verified full backups and the associated restore software available before running any script or programming example. Use these scripts and programming examples entirely at your own risk. All liability claims against the author in relation to material or non-material losses caused by the use, misuse or non-use of the information provided, or the use of incorrect or incomplete information, are excluded. All content is subject to change and provided without obligation.

 Back to the ICT-Hotlist...
Back to the ICT-Hotlist...